12. Challenge: Shortest Path

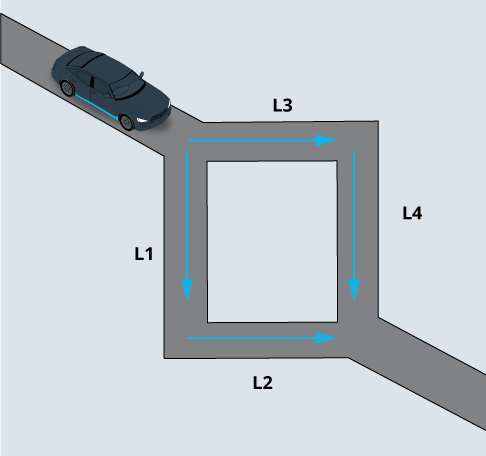
Carla's at a fork in the road and she insists on making the optimal choice for which way to go. This is a classic example of a search problem. In this situation, the optimal path is the shortest path.
Carla has two choices:
Go Left - in which case she will travel a total distance of
L3 + L4.Go Right - in which case she will travel a total distance of
L1 + L2.
Complete the function below so that it returns the string L when option 1 is a shorter distance and returns the string R when option 2 is shorter. If the two options are the same it can return either L or R.
Start Quiz:
User's Answer:
(Note: The answer done by the user is not guaranteed to be correct)